Treatment for PAD

After careful review of your imaging, our subspecialty trained physicians determine a treatment plan for your PAD. It begins with a diagnostic angiogram. An angiogram is a minimally invasive surgical procedure where a catheter is directed into the arteries of your arms of legs and contrast dye is injected to evaluate the blood flow.
Once the angiogram is completed, the physician can come up with an adequate treatment plan. The methods we have to treat peripheral arterial disease at TRA include angioplasty, atherectomy, and stent placement.
Angioplasty
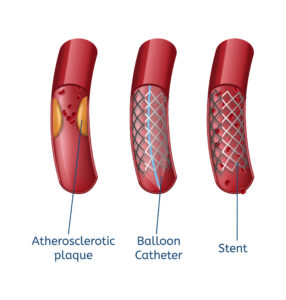
The basic procedure of angioplasty involves placing a small balloon into an area of blood vessel narrowing and then slowly expanding it to push the plaque out of the way. This is done in a controlled fashion to improve the size of the blood vessel and not cause damage to the vessel.
Atherectomy
Atherectomy is a procedure which debulks the plaque that has built up in your arteries. A variety of devices are used to either shave off the plaque, mince the plaque into tiny pieces, or break it down and pull it out of your blood vessels.
 Stent placement
Stent placement
Stents are sometimes needed to treat arteries that have not responded to the initial therapies of angioplasty and atherectomy. A stent is a metal tube that props open your artery. Some stents are made of just metal, and some are made of metal and a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) cover.
Aftercare
After the procedure, your doctor will use a small plug to close the hole in your artery through which the surgery has been performed. You will recover from the sedation medications used during the procedure while laying flat for a few hours. After a few hours of bedrest, you will be able to go home with a driver.
Most patients are placed on a blood thinner after the procedure for a short time to keep their arteries open. You may have a follow up clinic appointment in 1-2 weeks to assess healing and check the wound site.
Interested in learning more? Visit the Vein and Vascular section of our website.
